Oral leukoplakia
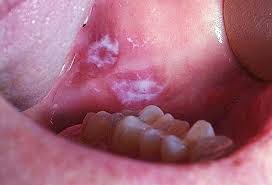
Leukoplakia (leuko-white; plakia-patch) Oral leukoplakia is defined by the WHO as “a white patch or plaque that cannot be scrapped off and also characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease”. Etiology Chemical: alcohol, tobacco mechanical: sharp tooth or crown margins, irritating denture clasps Premalignant epithelial changes Candida Albicans Ultraviolet radiation Trauma Toothpaste or mouth rinses (sanguinaria) Etiology continued Acute candidiosis Thrush Acute antibiotic stomatitis Chronic Denture induced stomatitis Chronic hyperplasia or mucocutaneous candidiosis Erythematous candidiosis Leukoplakia: Clinical Features 1. Affects 1.5 – 12% of total population 2. It usually affects people over the age of 40...
Comments
Post a Comment