Oral leukoplakia
Leukoplakia (leuko-white; plakia-patch) Oral leukoplakia is defined by the WHO as “a white patch or plaque that cannot be scrapped off and also characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease”.
- Etiology Chemical: alcohol, tobacco mechanical: sharp tooth or crown margins, irritating denture clasps Premalignant epithelial changes Candida Albicans Ultraviolet radiation Trauma Toothpaste or mouth rinses (sanguinaria)
- Etiology continued Acute candidiosis Thrush Acute antibiotic stomatitis Chronic Denture induced stomatitis Chronic hyperplasia or mucocutaneous candidiosis Erythematous candidiosis
- Leukoplakia: Clinical Features 1. Affects 1.5 – 12% of total population 2. It usually affects people over the age of 40 years (average age is 60 years). 3. Prevalence increases rapidly with age particularly in males. 4. Approximately 8 % of the males over the age of 70 years are reportedly affected. 5. 17-25 % carcinoma in situ. 6. 5.4% may develop squamous cell carcinoma in smokers it rises to 16%
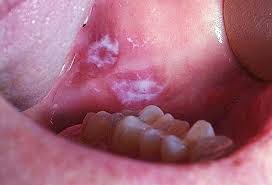
- . Sites of predilection Lateral and ventral tongue floor of the mouth alveolar ridge mucosa corner of the mouth less frequently: soft palate lip
- Site % of leukoplakia at this site % of leukoplakia at this site that show dysplasia or carcinoma Mandibular mucosa and sulcus 25.2 14.6 Buccal musosa 21.9 16.5 Maxillary mucosa and sulcus 10.7 14.8 Palate 10.5 18.8 Lips 10.3 24.0 Floor of the mouth 8.6 42.9 tongue 6.8 24.2 retromolar 5.9 11.7
- Lesions with dysplasia or carcinoma None – 80% Mild – 12% severe – 5% Carcinoma – 3%
- Variants Early or Thin Leukoplakia Thick Leukoplakia Granular Leukoplakia Verruciform Leukoplakia Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia
- Clinical Forms Homogenous Non Homogenous (speckled)
- Homogenous Uniform flat appearance that may exhibit shallow cracks and has a smooth, plaque like, wrinkled or corugated surface with a consistent texture throughout
- Non Homogenous A predominantly white or white and red lesion (erythroleukoplakia). Area of redness and ulceration Irregularly flat, nodular thickening and exophytic Nodular lesions have raised, rounded red and or white excrescences
- HOMOGENOUS LEUKOPLAKIA NONHEMOGENOUS LEUKOPLAKIA
- Leukoplakia: A Premalignant or Precancerous Lesion Although leukoplakia is not associated with a specific histopathologic diagnosis, it is considered to be a premalignant lesion for the risk of malignant transformation is greater in a leukoplakic lesion than that associated with normal or unaltered mucosa.
- Malignant Transformation Potential Overall - 1 – 5% Homogenous - 0% Non Homogenous - 26%
- HISTOPATHOLOGY Hyperkeratosis Acanthosis Atrophy Atypia Dysplasia Inflammation
- Differential diagnosis Reactive Neoplastic Infections Immune mediated Heriditary Idiopathic Hyperkeratosis Epithelial dysplasia Chronic hyperplastic candidiosis Lichen planus Leukoedema Hairy tongue Acanthosis Carcinoma in situ Hairy leukoplakia Lupus erythematosus White sponge nevus Geographic tongue Actinic Chelitis Squamous cell carcinoma Syphilitic mucous patch Snuff dippers’s keratosis Verrucous Carcinoma Nicotine stomatitis
- Removable and fixed lesions Removable: ● Acute Pseudomembraneous Candiosis ● Chemical burns ● Plaqueand food debris ● Smoken tobacco keratosis Fixed ● Frictional (traumatic) keratosis ● Lichen planus ● Leukoplakia ● Smokers keratosis ● Chronic hyperplastic ● White sponge
- Prognosis Most white patches are harmless. If a patch persists, it may contain pre-cancerous or cancerous cells. The prognosis will depend on what type of cancer it is and whether it has spread.
Comments
Post a Comment