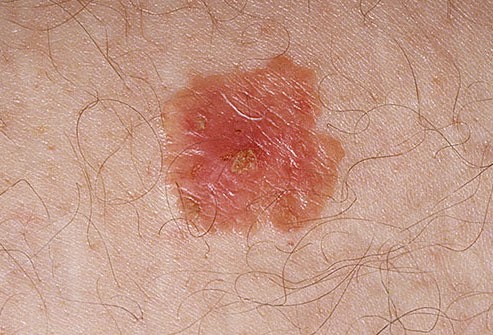
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. The two most common types are basal cell cancer and squamous cell cancer. They usually form on the head, face, neck, hands, and arms. Another type of skin cancer, melanoma, is more dangerous but less common. Anyone can get skin cancer, but it is more common in people who Have light-colored skin, hair and eyes Have a family member with skin cancer Spend a lot of time in the sun or have been sunburned Are over age 50 You should have your doctor check any suspicious skin markings and any changes in the way your skin looks. Treatment is more likely to work well when cancer is found early. If not treated, some types of skin cancer cells can spread to other tissues and organs. Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy (PDT), and biologic therapy. PDT uses a drug and a type of laser light to kill cancer cells. Biologic therapy boosts your body's own ability to fig...